Unified Gateway Installation & Management Centrally via MP
This document focuses on the Unified Gateway installation & management centrally via TSB Management Plane using the new MP Install Gateway Template resource and the Gateway Install resource.
This feature is currently in alpha and may undergo changes in future releases. It is not recommended for production use.
Introduction
TSB Management Plane supports creating Install Gateway Template resources at the organization level to streamline gateway deployment across your infrastructure. These organization-level templates serve as base configurations that define standard gateway settings, security contexts, resource allocations, and other operational parameters that should be consistently applied across your clusters.
When application teams create TSB gateway configurations, the Management Plane automatically references the appropriate gateway templates during translation based on cluster characteristics such as cloud provider, cluster labels, and other selectors. The template settings are then merged and applied during the creation of Kubernetes resources in the target cluster, ensuring consistent, secure, and optimized gateway deployments without requiring each team to define infrastructure-level configurations.
This approach provides:
- Centralized governance: Platform teams define standard configurations once at the org level
- Consistency: Gateway deployments inherit appropriate settings based on their environment
- Flexibility: Application teams can override specific properties when needed for their use cases
- Reduced complexity: Development teams focus on application routing without infrastructure concerns
How Gateway Deployment Using Templates Works?
Understanding when and where the physical ingress gateway infrastructure is deployed is crucial — here’s how it works:
The physical ingress gateway pod is deployed in the namespace of an application service that’s part of a TSB Workspace, when a Gateway resource is created for that service.
Here's the complete flow:
- Template Creation: Platform teams create Install Gateway Template resources at the organization level with environment or cluster-specific selectors
- Gateway Configuration: Application teams create a Gateway resource defining routing rules and hostnames, under the TSB
Workspaceconfigured for their service namespace - Template Matching: TSB Management Plane matches the target cluster's characteristics (cloud provider, labels) with the appropriate templates
- Translation: TSB Management Plane translates the
Gatewaydeployment configuration, merging it with the matched template's settings (HPA, security context, service type, etc.) - Propagation: The translated Gateway deployment configuration is propagated by Global Control Plane (XCP Central) to the target clusters
- Deployment: The Local Control Plane (XCP Edge) deploys the actual gateway infrastructure (pods, services, HPA) into the service's namespace as Kubernetes resources
InstallGatewayTemplate Resource
The InstallGatewayTemplate resource defines the standard configuration for gateways in your organization:
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: InstallGatewayTemplate
metadata:
name: base-igw-template
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
spec:
displayName: "Base Ingress Gateway Template"
description: "Template for ingress gateways deployed across all clusters"
allClustersSelector: true
gatewaySpec:
type: INGRESS
kubeSpec:
service:
type: LoadBalancer
deployment:
hpaSpec:
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 12
resources:
requests:
memory: "256Mi"
cpu: "200m"
limits:
memory: "1Gi"
cpu: "1000m"
podSecurityContext:
fsGroup: 65535
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefault
supplementalGroups:
- 65535
containerSecurityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
privileged: false
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
runAsGroup: 65535
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 65535
Template Types
TSB mainly supports three types of template selectors, allowing you to create templates that apply across different scopes within your organization.
Environment-Specific Templates
Environment-specific templates target gateways based on cloud provider or infrastructure type. This allows you to define provider-specific configurations such as load balancer types, security contexts, or resource limits that align with each cloud platform's best practices.
AKS Template Example
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: InstallGatewayTemplate
metadata:
name: aks-gw-template
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
spec:
displayName: "AKS Ingress Gateway Template"
description: "Template for Ingress gateways deployed on AKS"
environmentSelector:
provider: "aks"
gatewaySpec:
type: INGRESS
kubeSpec:
service:
type: LoadBalancer
deployment:
hpaSpec:
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 12
Cluster-Specific Template
Cluster-specific templates apply to gateways based on cluster labels and properties. This is useful when you have specific clusters that require unique configurations, such as dedicated clusters for high-memory workloads or specific teams.
Once you tag the clusters in TSB using custom labels, you can use the same labels in the Template as a selection criteria.
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: InstallGatewayTemplate
metadata:
name: payment-cluster-template
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
spec:
displayName: "Payment Team Cluster Template"
description: "Template for gateways in payment team clusters"
clusterSelector:
labels:
team: "payment"
namespaceSelector:
labels:
mem: "high"
gatewaySpec:
type: INGRESS
kubeSpec:
deployment:
hpaSpec:
minReplicas: 3
maxReplicas: 20
resources:
requests:
memory: "512Mi"
cpu: "500m"
limits:
memory: "2Gi"
cpu: "2000m"
All-Cluster Template
All-cluster templates serve as organization-wide base configurations that apply to all gateways unless overridden by more specific MP Gateway Install resource.
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: InstallGatewayTemplate
metadata:
name: org-wide-gw-template
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
spec:
displayName: "Organization-Wide Gateway Template"
description: "Base template for all gateways across the organization"
allClustersSelector: true
gatewaySpec:
type: UNIFIED
kubeSpec:
deployment:
podSecurityContext:
fsGroup: 65535
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefault
containerSecurityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
privileged: false
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 65535
How to Use InstallGatewayTemplates?
This example demonstrates how gateway templates automatically apply to application gateways across different clusters based on the cloud provider.
Setup Overview
This is what we are going to do:
- Create an organization-wide gateway template specific to the
gkecloud provider - Onboard two control plane clusters:
c1andc2 - Deploy applications with gateway configurations in each cluster
- Observe how the gateway template automatically provisions gateway infrastructure
Cluster C1
- Deploy
bookinfoapplication in thepaymentnamespace - Create Tenant
paymentand workspacepayment-wswith the selector asc1/payment - Define gateway configuration to expose
bookinfo.tetrate.iowithout an install resource
Cluster C2
- Deploy
httpbinapplication in themarketingnamespace - Create Tenant
marketingand workspacemarketing-wswith the selector asc2/marketing - Define gateway configuration to expose
httpbin.tetrate.iowithout an install resource
Step 1: Create the GKE Gateway Template
Create the InstallGatewayTemplate resource under the Organization for provider gke.
- tctl
- kubectl (GitOps)
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: InstallGatewayTemplate
metadata:
name: gke-gw-template
organization: tetrate
spec:
displayName: "GKE Ingress Gateway Template"
description: "Template for Ingress gateways deployed on GKE"
environmentSelector:
provider: "gke"
gatewaySpec:
type: INGRESS
kubeSpec:
service:
type: LoadBalancer
deployment:
hpaSpec:
minReplicas: 2
podSecurityContext:
fsGroup: 65535
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefault
supplementalGroups:
- 65535
containerSecurityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
privileged: false
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
runAsGroup: 65535
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 65535
tctl apply -f gke-gw-template.yaml
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: InstallGatewayTemplate
metadata:
name: gke-gw-template
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
spec:
displayName: "GKE Ingress Gateway Template"
description: "Template for Ingress gateways deployed on GKE"
environmentSelector:
provider: "gke"
gatewaySpec:
type: INGRESS
kubeSpec:
service:
type: LoadBalancer
deployment:
hpaSpec:
minReplicas: 2
podSecurityContext:
fsGroup: 65535
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefault
supplementalGroups:
- 65535
containerSecurityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
privileged: false
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
runAsGroup: 65535
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 65535
kubectl apply -f gke-gw-template.yaml
Step 2: Deploy to Cluster C1 (Payment Team)
Create the payment Tenant and other TSB resources along with the gateway configuration to expose bookinfo.tetrate.io:
- tctl
- kubectl (GitOps)
- apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Tenant
metadata:
name: payment
organization: tetrate
spec:
displayName: Payment
- apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
name: payment-ws
organization: tetrate
tenant: payment
spec:
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "c1/payment"
displayName: payment-ws
- apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Group
metadata:
name: payment-gg
organization: tetrate
tenant: payment
workspace: payment-ws
spec:
displayName: Payment Gateway Group
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "c1/payment"
configMode: BRIDGED
- apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: bookinfo-ig
organization: tetrate
tenant: payment
workspace: payment-ws
gatewayGroup: payment-gg
spec:
displayName: Bookinfo Ingress
workloadSelector:
namespace: payment
labels:
app: bookinfo-ingress-gateway
http:
- hostname: bookinfo.tetrate.io
name: bookinfo-tetrate
port: 80
routing:
rules:
- route:
serviceDestination:
host: "payment/productpage.payment.svc.cluster.local"
port: 9080
tctl apply -f payment-conf.yaml
- apiVersion: tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Tenant
metadata:
name: payment
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
spec:
displayName: Payment
- apiVersion: tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
name: payment-ws
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: payment
spec:
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "c1/payment"
displayName: payment-ws
- apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Group
metadata:
name: payment-gg
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: payment
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: payment-ws
spec:
displayName: Payment Gateway Group
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "c1/payment"
configMode: BRIDGED
- apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: bookinfo-ig
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: payment
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: payment-ws
tsb.tetrate.io/gatewayGroup: payment-gg
spec:
displayName: Bookinfo Ingress
workloadSelector:
namespace: payment
labels:
app: bookinfo-ingress-gateway
http:
- hostname: bookinfo.tetrate.io
name: bookinfo-tetrate
port: 80
routing:
rules:
- route:
serviceDestination:
host: "payment/productpage.payment.svc.cluster.local"
port: 9080
kubectl apply -f payment-conf.yaml
Observe the Gateway Deployments Triggered by the Gateway Resource
When you created the gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/bookinfo-ig resource above, the TSB Management Plane matched it with the GKE template, translated the configuration, propagated into target cluster by Global Control Plane and XCP Edge running on control plane cluster deployed the physical gateway infrastructure into the payment namespace.
Note that during translation, the gateway deployment resource inherits properties like security context, HPA and other settings from the GKE template. Let's verify this:
You can verify the status of gateway deployment via TSB UI
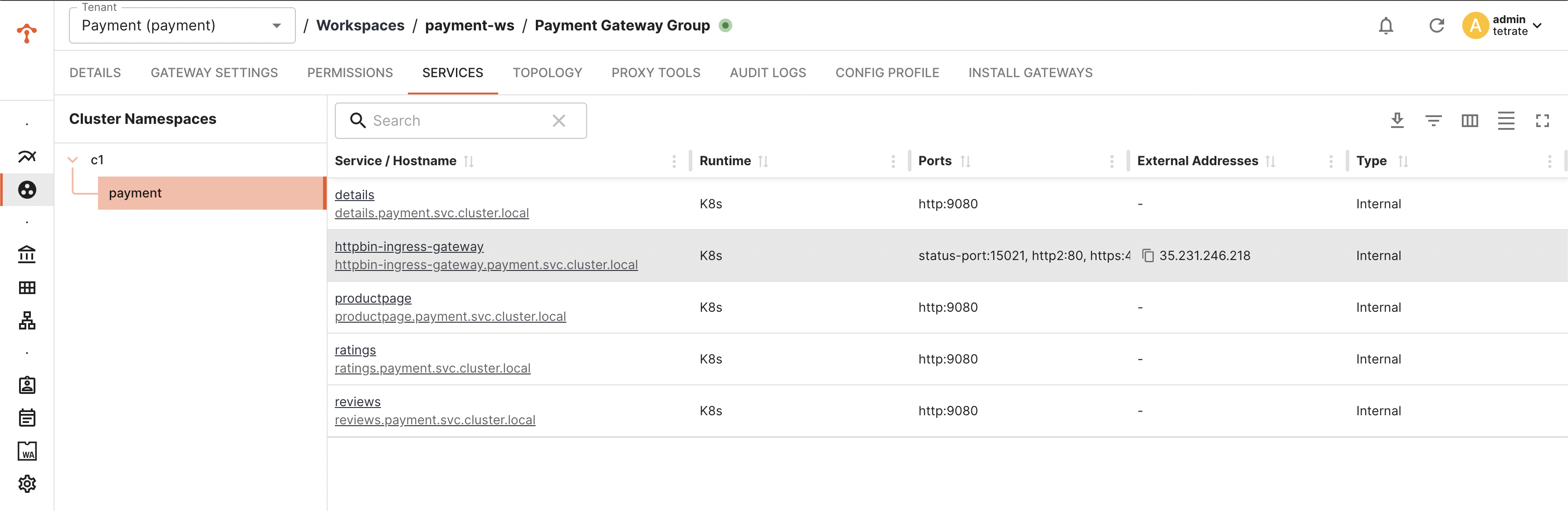
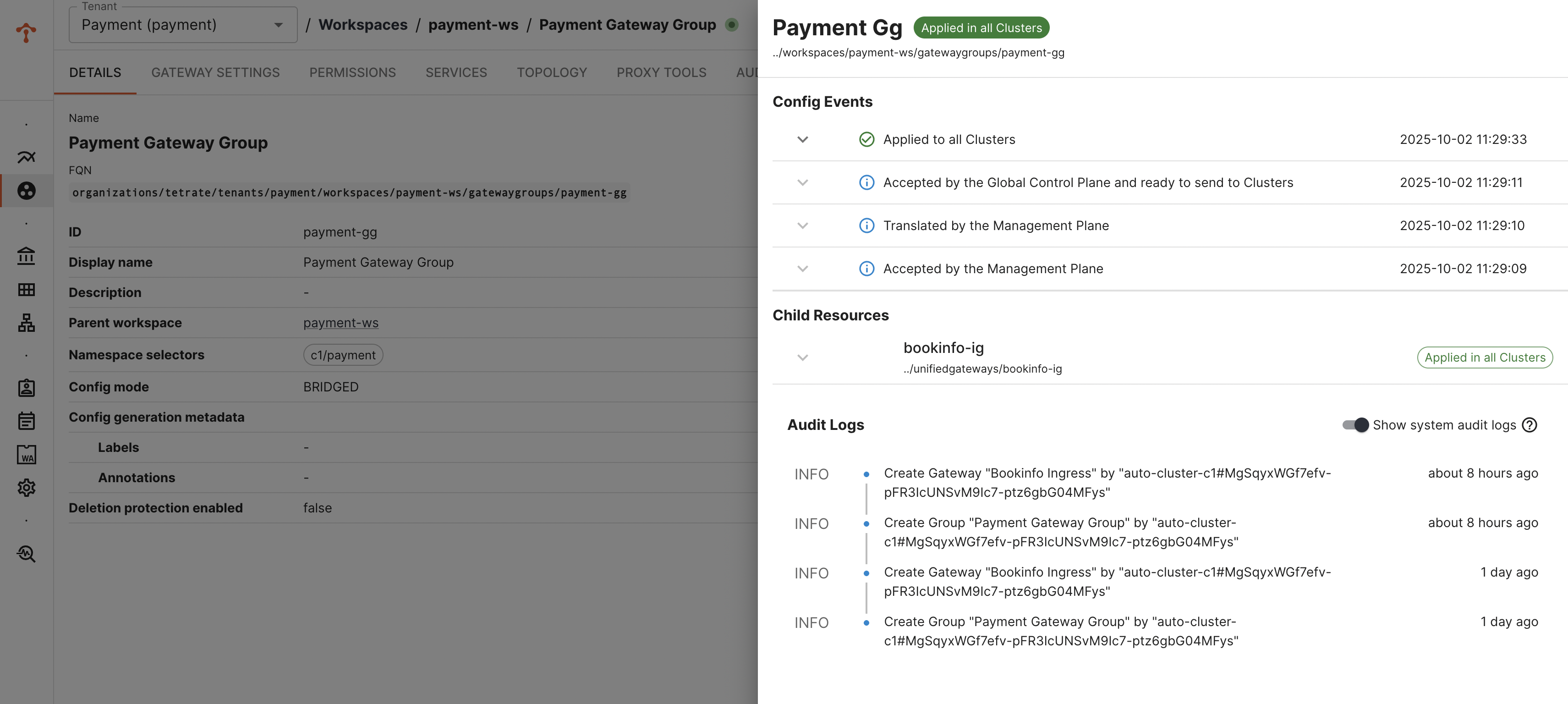
Verify the K8s Resources Deployed in the Target Cluster
Note: Name of the deployment, service and other kube resources would be taken from the labels.app configured in Gateway configuration. Verify number of replicas, security context settings are inherited and applied as per the gke template.
kubectl get all -n payment
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/bookinfo-ingress-gateway-568bc57bc8-wkzhw 1/1 Running 0 21m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/bookinfo-ingress-gateway LoadBalancer 172.24.144.118 35.231.246.218 15021:32276/TCP,80:31401/TCP,443:32117/TCP 21m
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/bookinfo-ingress-gateway 1/1 1 1 21m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/bookinfo-ingress-gateway-568bc57bc8 1 1 1 21m
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/bookinfo-ingress-gateway Deployment/bookinfo-ingress-gateway cpu: 4%/75% 2 10 1 21m
Step 3: Deploy to Cluster C2 (Marketing Team)
Create the marketing Tenant and TSB resources along with the gateway configuration to expose httpbin.tetrate.io:
- tctl
- kubectl (GitOps)
- apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Tenant
metadata:
name: marketing
organization: tetrate
spec:
displayName: marketing
- apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
name: marketing-ws
organization: tetrate
tenant: marketing
spec:
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "c2/marketing"
displayName: marketing-ws
- apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Group
metadata:
name: marketing-gg
organization: tetrate
tenant: marketing
workspace: marketing-ws
spec:
displayName: marketing Gateway Group
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "c2/marketing"
configMode: BRIDGED
- apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: httpbin-ingress-gateway
organization: tetrate
tenant: marketing
workspace: marketing-ws
gatewayGroup: marketing-gg
spec:
displayName: Httpbin Ingress
workloadSelector:
namespace: marketing
labels:
app: httpbin-ingress-gateway
http:
- hostname: httpbin.tetrate.io
name: httpbin-tetrate
port: 80
routing:
rules:
- route:
serviceDestination:
host: "marketing/httpbin.marketing.svc.cluster.local"
port: 8000
tctl apply -f marketing-tsb-conf.yaml
- apiVersion: tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Tenant
metadata:
name: marketing
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
spec:
displayName: marketing
- apiVersion: tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
name: marketing-ws
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: marketing
spec:
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "c2/marketing"
displayName: marketing-ws
- apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Group
metadata:
name: marketing-gg
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: marketing
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: marketing-ws
spec:
displayName: marketing Gateway Group
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "c2/marketing"
configMode: BRIDGED
- apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: httpbin-ingress-gateway
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: marketing
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: marketing-ws
tsb.tetrate.io/gatewayGroup: marketing-gg
spec:
displayName: Httpbin Ingress
workloadSelector:
namespace: marketing
labels:
app: httpbin-ingress-gateway
http:
- hostname: httpbin.tetrate.io
name: httpbin-tetrate
port: 80
routing:
rules:
- route:
serviceDestination:
host: "marketing/httpbin.marketing.svc.cluster.local"
port: 8000
kubectl apply -f marketing-tsb-conf.yaml
Observe the Gateway Deployments Triggered by the Gateway resource
When you created the gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/httpbin-ingress-gateway resource above, the TSB Management Plane matched it with the GKE template, translated the configuration, propagated into target cluster by Global Control Plane and XCP Edge running on the control plane cluster deployed the physical gateway infrastructure into the marketing namespace.
Note that during translation, the gateway deployment resource inherits properties like security context, HPA and other settings from the GKE template. Let's verify this:
You can verify the status of gateway deployment via TSB UI
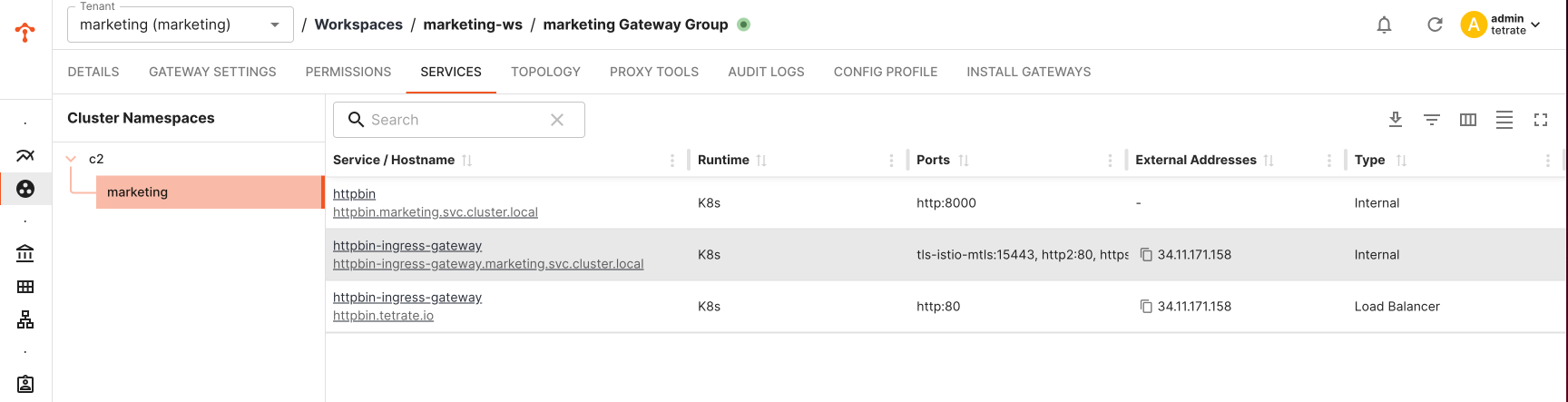
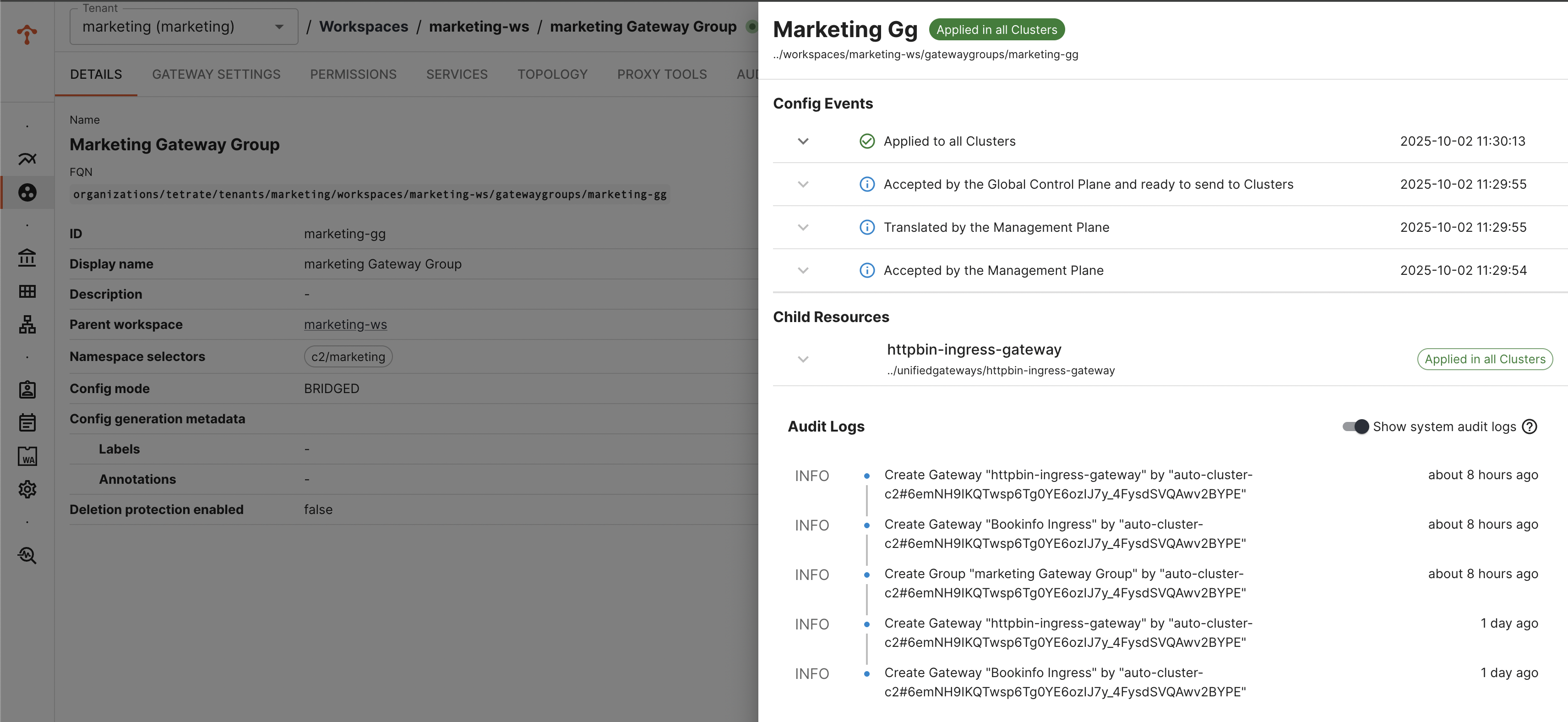
Verify the K8s Resources Deployed in the Target Cluster
Note: Name of the deployment, service and other kube resources would be taken from the labels.app configured in Gateway configuration. Verify num of replicas, security context settings are inherited and applied as per the gke template.
kubectl get all -n marketing
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/httpbin-ingress-gateway-54f64bf654-8mz26 1/1 Running 0 6s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/httpbin-ingress-gateway LoadBalancer 172.25.171.125 <pending> 15021:32397/TCP,80:30182/TCP,443:32420/TCP 9s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/httpbin-ingress-gateway 1/1 1 1 11s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/httpbin-ingress-gateway-54f64bf654 1 1 1 12s
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/httpbin-ingress-gateway Deployment/httpbin-ingress-gateway cpu: <unknown>/75% 1 10 0 14s
Overriding Template Properties with MP Install Resources
While organization-level templates provide consistent baseline configurations, there are scenarios where application-specific requirements necessitate customization. TSB allows you to override template properties by creating Management Plane Gateway Install resources alongside your application gateway configurations.
When to Use Application Specific Overrides
Override capabilities are particularly useful for:
- Scale requirements: Applications expecting higher traffic volumes need increased replica counts
- Performance tuning: Specific workloads requiring different resource allocations
- Regulatory compliance: Specific applications requiring additional security constraints
Override Example: Scaling for High Traffic
In this example, the marketing team anticipates a promotional campaign that will significantly increase traffic to their httpbin service.
Rather than modifying the organization-wide template (which would affect all gateways), they can create an MP install resource to scale only their specific gateway.
Create the override MP install resource:
- tctl
- kubectl (GitOps)
apiVersion: install.tetrate.io/v1alpha1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: httpbin-ingress-gateway
organization: tetrate
tenant: marketing
workspace: marketing-ws
gatewayGroup: marketing-gg
spec:
type: INGRESS
targetCluster: c2
targetNamespace: marketing
kubeSpec:
deployment:
labels:
app: httpbin-ingress-gateway
hpaSpec:
minReplicas: 4
tctl apply -f httpbin-gw-install.yaml
apiVersion: install.tetrate.io/v1alpha1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: httpbin-ingress-gateway
namespace: marketing
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: marketing
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: marketing-ws
tsb.tetrate.io/gatewayGroup: marketing-gg
spec:
type: INGRESS
targetCluster: c2
targetNamespace: marketing
kubeSpec:
deployment:
labels:
app: httpbin-ingress-gateway
hpaSpec:
minReplicas: 4
kubectl apply -f httpbin-gw-install.yaml -n marketing
The targetCluster and targetNamespace fields provide granular control to target specific application gateway deployments for overrides. This precision ensures that your configuration changes apply only to the intended gateway in the specific cluster and namespace, preventing unintended impacts on other gateways that may share similar names or characteristics across your multi-cluster environment.
Verify the updated configuration
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/httpbin-ingress-gateway-5466ddf675-5ldx5 1/1 Running 0 14m
pod/httpbin-ingress-gateway-5466ddf675-s5kvq 1/1 Running 0 14m
pod/httpbin-ingress-gateway-5466ddf675-txvw2 1/1 Running 0 14m
pod/httpbin-ingress-gateway-5466ddf675-v8rwt 1/1 Running 0 14m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/httpbin-ingress-gateway LoadBalancer 172.25.171.125 34.123.45.67 15021:32397/TCP,80:30182/TCP,443:32420/TCP 14m
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/httpbin-ingress-gateway 4/4 4 4 14m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/httpbin-ingress-gateway-5466ddf675 4 4 4 14m
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/httpbin-ingress-gateway Deployment/httpbin-ingress-gateway cpu: 4%/75% 4 10 4 14m
The gateway now runs with 4 minimum replicas instead of the template's default of 2, providing additional capacity for the anticipated traffic increase while maintaining all other template configurations (security context, max replicas, service type, etc.).
Advanced: Template Priority and Configuration Merging
For sophisticated scenarios, TSB supports defining multiple templates at the organization level with different priorities and workload selectors. This enables layered configuration strategies where you can establish baseline standards and apply targeted overrides for specific gateways.
How Template Precedence Works?
During the translation phase, TSB determines the merge order for templates that match a gateway based on their selector precedence and the priority field. The following precedence rules are applied:
- MP Gateway Install Resource has the highest precedence and always takes priority. It is intended for application-specific overrides.
- Template selector precedence (from highest to lowest):
- Cluster selectors with namespace selector matching a namespace name (most specific)
- Cluster selectors with namespace selector matching labels
- Cluster selectors with no namespace selector
- Environment selectors
- AllClusters selectors (least specific)
- Priority field: When two or more templates share the same selector precedence, the priority field determines the merge order. Lower numerical priority values take precedence (priority 1 wins over priority 100).
For example, a template with an AllClusters selector and priority 1 will override another AllClusters template with priority 100. However, it will always be overridden by any template with a more specific selector (such as an environment or cluster selector), regardless of that template's priority value.
The final configuration is therefore the result of merging all matching templates according to their selector precedence and priority.
Example: Layered Configuration Strategy
Consider a scenario where you need to:
- Apply a baseline configuration across all clusters
- Override settings for high-traffic gateways
- Maintain the ability for application teams to make specific adjustments
Baseline Template (Low Priority):
Create a base template with low priority (higher numerical value) that applies standard settings across all gateways:
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: InstallGatewayTemplate
metadata:
name: base-traffic-template
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
spec:
displayName: "Base Traffic Template"
description: "Baseline configuration for all gateways"
allClustersSelector: true
priority: 100 # Low priority (higher number)
gatewaySpec:
kubeSpec:
deployment:
hpaSpec:
minReplicas: 2
maxReplicas: 10
resources:
requests:
memory: "256Mi"
cpu: "200m"
Result: All ingress gateways across all clusters will be deployed with minReplicas: 2 by default.
High-Traffic Template (High Priority):
Create a targeted template with higher priority (lower numerical value) that overrides settings for specific gateways:
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: InstallGatewayTemplate
metadata:
name: high-traffic-ingress-gateway-template
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
spec:
displayName: "High Traffic Ingress Gateway Template"
description: "Enhanced configuration for high-traffic ingress gateways"
allClustersSelector: true
priority: 1 # High priority (lower number)
gatewayWorkloadSelector:
labelsSelector:
labels:
app: "ingress-gateway-high-traffic"
gatewaySpec:
kubeSpec:
deployment:
hpaSpec:
minReplicas: 4
maxReplicas: 20
resources:
requests:
memory: "512Mi"
cpu: "500m"
Result: Across all clusters:
- Most gateways will have
minReplicas: 2and basic resource allocations from the base template - Only gateways labeled with
app: "ingress-gateway-high-traffic"will haveminReplicas: 4and enhanced resources - The higher priority template overrides only the specified fields (minReplicas, maxReplicas, resources)
- Other properties from the base template (security context, service type, etc.) remain inherited
Application-Specific Override with MP Install Resource:
If the marketing team needs even more replicas for a promotional event, they can create an MP Install resource:
apiVersion: install.tetrate.io/v1alpha1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: httpbin-ingress-gateway
namespace: marketing
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: marketing
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: marketing-ws
tsb.tetrate.io/gatewayGroup: marketing-gg
spec:
type: INGRESS
targetCluster: c2
targetNamespace: marketing
kubeSpec:
deployment:
labels:
app: httpbin-ingress-gateway
hpaSpec:
minReplicas: 8
Final Result:
- The
httpbin-ingress-gatewaywill haveminReplicas: 8(MP Install resource overrides) - Enhanced resource allocations from the high-priority template are retained
- Baseline security context and other settings from the base template are still applied
Summary
The Unified Gateway Lifecycle Management via Management Plane in TSB provides a powerful framework for standardizing gateway deployments while maintaining the flexibility needed for application-specific requirements. By leveraging organization-level templates with selective overrides, teams can achieve consistency, security, and operational efficiency across their service mesh infrastructure.